From the Resene ProSelect Technical Information Centre
Testing abrasion resistance of coatings has always presented difficulties to coating developers, primarily because mimicking natural abrasion and wear in laboratory tests does not fully account for the wide range of wear conditions found in the field. A wide range of laboratory tests have been used to simulate wear but correlation with field wear is not always accurate and the results are best used for comparative purposes.
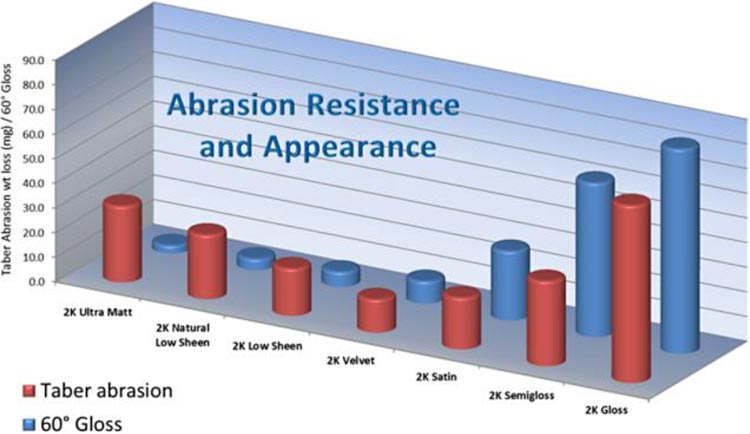
The most popular abrasion test (with a large number of variants) is the Taber abrasion test. Results from this test are widely reported for a range of coatings and indicate the resistance of a coating to wear – specifically loss of coating thickness during heavy use. While popular, the test is dominated by wear modes that are not typical of field use and fails to take into account the appearance of a coating after abrasion occurs. Other more appropriate methods have been sought and currently the most appropriate is a modification of a well established test in the textile industry, the Martindale Abrasion test. This test focuses on the appearance of a coating after abrasion and is appropriate for surfaces such as hardwood floors, where appearance is one of the most important elements.
The TABER Abraser (Abrader) is used to perform accelerated wear testing. Referenced in numerous international standards, materials include plastics, coatings (including flooring polyurethane coatings), laminates, leather, paper, ceramics, carpeting, safety glazing etc. While this is a good “tool” to help establish wear properties, it does not necessarily show actual performance of floor polyurethane, with regard to other critical factors. When it comes to viewing applied floor coatings such marring, scratching and burnishing are properties that can “degrade the floors appearance, but these cannot be measured using the Taber Test. These properties are different but affect how the floor looks to the viewer.
| ProSelect | Taber wt loss (mg) |
|---|---|
| Gloss | 72 |
| Semi-gloss | 34 |
| Satin | 21 |
| Velvet | 13 |
| Low Sheen | 19 |
| Natural Low Sheen | 26 |
| Ultra Matt | 31 |
| Gloss Moisture Cure (MC) | 24 |
| Competitor (semigloss) W/B | 53 |
Testing Details: ISO 7784–2
CS-17 wheels, 1 kg weight per wheel, 1000 cycles at 23°C and 50% RH.
The Taber test equipment is illustrated below
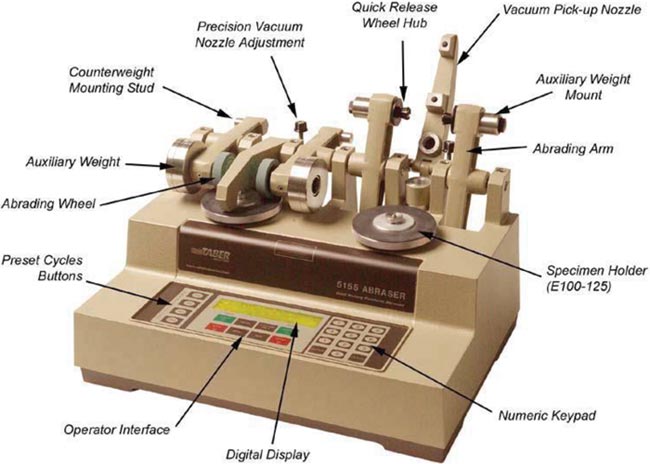
More information on the process of testing can be found on the AFTA Taber Testing Information Sheet #32
The Martindale method simulates natural wear where the test sample is rubbed against a standard abrasive surface with a specified force. A rub pattern (called a Lissajous pattern named after the French physicist Jules Antoine Lissajous) consisting of numerous different elliptical paths is used and the pattern is repeated a number of times, before being rated using a standardised reference chart. Many variations of the test of the test are possible although standardised methods have been adopted in Europe. The test procedure used for Resene ProSelect is based on the European test method CEN TC 207 and uses 10 Lissajous patterns of an abrasive pad with a 6 N load.
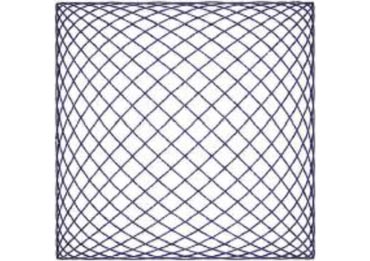


| Product | Martindale rating |
|---|---|
| ProSelect | |
| Gloss | 4 |
| Semigloss | 3-4 |
| Satin | 3 |
| Velvet | 2-3 |
| Low Sheen | 2 |
| Ultra Matt | 2 |
| Competitor | |
| Competitor (semigloss) W/B | 2-3 |
| Gloss Moisture cure (MC) | 4-5 |
| Numerical rating | Scratch picture | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 5 |  |
No visible scratches or only few scratches. No matt area. |
| 4 |  |
Visible scratches. Lissajous figure (square) not visible. No matt area. |
| 3 |  |
Many visible scratches. Lissajous figure (square) partly visible. No matt area. |
| 2 |  |
Many visible scratches. Lissajous figure/figures visible, and/or small matt abraded area. |
| 1 |  |
Many visible scratches. Lissajous figure/figures visible, and/or large matt abraded area. |
Rating chart used for ProSelect Martindale Abrasion testing
Access routes must have “adequate slip-resistant walking surfaces under all conditions of normal use. Exceptions include the interior of residential houses or where safety matting is provided. Acceptable solutions for level walking surfaces are described in the NZ Building Code Acceptable Solutions and Verification Methods with reference to AS/NZS 4586 (2013).
A surface must either be tested to AS 4586 (2013) Appendix B and achieve a coefficient of friction greater than 0.40, or be of an appropriate type listed in the NZ Building Code. In practice almost all floorcoverings provide acceptable dry slip resistance, Resene ProSelect has been tested to confirm resulting surfaces exceed the minimum coefficient of friction.
Two methods are listed for compliance in the NZ Building Code.
ProSelect Anti-Slip additive is available to provide increased wet-slip resistance (see test results in the table below).
Increased slip resistance is required for these surfaces. A P4 rating is an acceptable solution for stairs and on ramps not steeper than 1:12. For steeper ramps consult AS/NZS 4586 (2013) which contains reference tables and a method to calculate the required wet-slip resistance.
NOTE: Transition zones between areas that will usually remain dry and areas that may become wet require extension of the wet-slip resistant walking surface and/or absorbent matting to be installed. Details are included in AS/NZS 4586 (2013) with typically at least 6 m of slip-resistant flooring required in such zones.
ProSelect Dry CoF (coefficient of friction) for a normal walking surface must be ≥0.40 and for stairs, sloping and wet areas a ProSelect wet slip resistance value of >39 must be achieved.
| With ProSelect Anti-Slip additive | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProSelect | Dry Slip Test CoF |
AS4586 Classification |
Wet Slip Test SRV |
Wet Slip P Rating |
Wet Slip Test SRV |
Wet Slip P Rating |
| Gloss | 0.50 | D1 | 11 | P0 | 48 | P4 |
| Semigloss | 0.45 | D1 | - | - | ||
| Satin | 0.50 | D1 | 15 | P1 | ||
| Velvet | 0.45 | D1 | 19 | P1 | ||
| Low Sheen | 0.60 | D1 | 32 | P2 | refer note on ProSelect Anti-Slip Data Sheet PS10 for more information |
|
| Natural Low Sheen | 0.75 | D1 | - | - | ||
| Ultra Matt | 0.70 | D1 | 45 | P4 | ||
Testing Details: AS 4586 - 2013
Substrate: Australian Oak (aka Victorian Ash / Tasmanian Oak)
Substrate Dimensions: 112 x 1200 mm (13 mm thick)
Coating: 2-component waterborne polyurethane; 3 x layers @ 25-30 microns dry film per coat
Anti-Slip Additive Test Results: ProSelect Anti-Slip added at 100 mL per Litre of Base
The Pendulum Test measure dynamic coefficient of friction (CoF). The test is designed to replicate a pedestrian heel strike, the point at which most slips occur.
The Pendulum Test can be used to accurately test the slip potential on clean and dry or contaminated floors. The test also work with dry contaminants.

More information on the process of testing can be found on the AFTA Understanding Slip Resistance Information Sheet #45
Timber samples are coated with three coats of Resene ProSelect finish and then cured for seven days at ambient temperature. Adhesion test results are based on AS 1580.408.4-1993 Adhesion (cross cut) Standard using Tesafix 4970 Tape @ 20 N/25mm strength and using an Elcometer 105 template at 2mm cut spacing.
| ProSelect Velvet | ProSelect Gloss | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Timber | Adhesion Result | Adhesion Result | General Notes |
| Jarrah | 0 | 0 | |
| Rimu | 0 | 0 | |
| Matai (recycled) | 0 | 0 | |
| Matai | 0 | 0 | |
| Totara | 0 | 0 | No degreasing / cleaning |
| Totara | 0 | 0 | Methylated spirits wipe |
| Totara | 0 | 0 | Turpentine wipe |
| Australian Oak* | 0 | 0 | |
| European Oak | 0 | 0 | |
| NZ Oak | 0 | 0 | European Oak planted by settlers |
| American White Oak | 0 | 0 | |
| Ash | 0 | 0 | |
| *aka Victorian Ash / Tasmanian Oak | |||
| ProSelect Velvet | ProSelect Gloss | ||
| Existing Coated Timber | Adhesion Result | Adhesion Result | General Notes |
| HD Polysatin - Alkyd Poly | 0 | 0 | Sanded with 120 g |
| Qrystal - Alkyd Poly | 0 | 0 | Sanded with 120 g |
| M/C Polyurethane | 0 | 0 | Sanded with 120 g |
| ProSelect Gloss | 0 | 0 | Sanded with 120 g |
| ProSelect Velvet | 0 | 0 | Sanded with 120 g |
TABLE 1
CLASSIFICATION OF TEST RESULTS
| Classification | Description | Appearance* |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | The edges of the cuts are completely smooth; none of the square of the lattice is detached. | 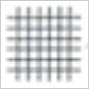 |
| 1 | Detachment of small flakes of the coating at the intersection of the cuts. A cross-cut area not directly greater than 5 percent is affected. | 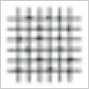 |
| 2 | The coating has flaked along the edges, at the intersections of the cuts, or at both locations. A cross-cut area distinctly greater than 5 percent, but not distinctly greater than 15 percent is affected. | 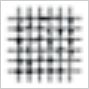 |
| 3 | The coating has flaked along the edges of the cuts partly or wholly in large ribbons, it has flaked partly or wholly on different parts of the squares, or both have occurred. A cross-cut area distinctly greater than 15 percent, but not distinctly greater than 35 percent is affected. | 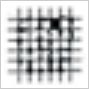 |
| 4 | The coating has flaked along the edges of the cuts in large ribbons, some squares have detached partly or wholly, or both have occurred. A cross-cut area distinctly greater than 35 percent, but not distinctly greater than 65 percent is affected. |  |
| 5 | Any degree of flaking greater than classification 4. | |
| * Appearance of surface of cross-cut area from which flaking has occurred (example for six parallel cuts) | ||
Resene ProSelect Technical Information Centre
Get a professional flooring finish on timber with Resene ProSelect